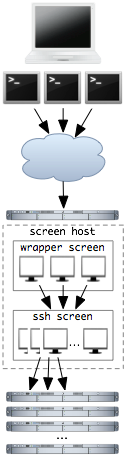
 I use GNU Screen to keep a few terminal windows open over a shared set of screen windows logged into a large number of other machines.
I use GNU Screen to keep a few terminal windows open over a shared set of screen windows logged into a large number of other machines.
Wrapper screen
I log in to the machine that will host my screens and start the wrapper screen.
screen -S wrapper -c .screenrc_wrapper
The wrapper screen's configuration just specifies the interrupt key.
escape ^Ww
I create a screen window in wrapper for each terminal window I want to use, as many as four. Each terminal window will run one of the wrapper windows.
SSH agent
I use SSH agent forwarding to log in to my screen host, but if you don't then you might need to run ssh-agent inside the wrapper screen before starting the ssh screen.
exec ssh-agent bash
ssh-add
This is necessary for the next step where I ssh into a bunch of other machines. I have already installed my public key on the destination machines.
SSH screen
I start the ssh screen from inside the wrapper screen.
screen -S ssh -c .screenrc_ssh
The ssh screen's configuration creates a bunch of windows that ssh into other machines I want to work on. I like to have at least two windows for each machine.
screen -t "host 1" ssh host1
screen -t "host 1" ssh host1
screen -t "host 2" ssh host2
screen -t "host 2" ssh host2
screen -t "host 3" ssh host3
screen -t "host 3" ssh host3
select 0
Inside the other wrapper windows, I attach to the running ssh screen.
screen -x ssh
At the start of the day, I open up a few terminal windows, log in into the screen server, and attach to the running wrapper screen. This is simplified with an alias.
alias wrapper='screen -x wrapper'